Obliczenia w kalkulatorze są orientacyjne. Bank
przygotuje dla Ciebie ostateczną ofertę, kiedy złożysz wniosek ratalny.

Domestic biological wastewater treatment plant METRIA SBR 2-4 with a capacity of 2500L, designed for up to 4 people.
| Capacity | 2500L |
| Length | 180cm |
| Width | 120cm |
| Height | 170cm |
| Inlet diameter | 160mm |
| Outlet diameter | 110mm |
| Manhole diameter | 615mm |
| Tank weight | 180 kg |
Domestic biological wastewater treatment plants METRIA SBR 2-4 are a modern solution to liquid waste problems in areas without access to a municipal sewage system. Their main advantages over traditional concrete septic tanks are:
Most treatment plants save around 6000 PLN annually, as they do not require monthly sludge removal like traditional septic tanks. In most domestic wastewater treatment plants, sludge removal is performed once a year or at most every two years, which saves both money and time. The variety of solutions and technologies allows for systems tailored to customer needs, soil conditions, and the appropriate drainage system.
The treatment plant operates on the basis of a primary settling tank (septic) and a biological reactor working in the batch SBR system (sequencing batch reactor).
The use of activated sludge technology dates back to 1914, introduced in England by Ardern and Lockett. The term activated sludge comes from the fact that during the treatment process, active masses of microorganisms are produced, capable of biologically decomposing organic matter.
In operation, biological wastewater treatment with activated sludge is achieved by feeding sewage into the reactor, where aerobic bacterial cultures are kept in suspension. After the appropriate reaction time, the treated wastewater is separated from the bacteria and discharged. In the reactor, bacteria break down organic compounds according to the reaction:
Organic matter + Oxygen + Nutrients + Microorganisms + New microorganisms + Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy for life
This allows for a very high reduction of pollutants in the outflow, ensuring reliable long-term performance. When combined with a drip irrigation system, it not only reduces costs but is also environmentally friendly.
The SBR technology first appeared in scientific literature in 1898, described by Thomas Wardle, and has been used for decades in both small and large facilities. The reactor operates in cycles of approximately 8 hours. Each cycle consists of:
· filling – period during which raw sewage is supplied to the batch reactor
· mixing – period during which the reactor contents are mixed without oxygen supply, creating anaerobic conditions
· aeration – period during which the reactor contents are aerated
· reaction – period during which aerobic biological processes occur.
· settling (sedimentation) – period during which the activated sludge undergoes sedimentation
· decanting – period during which treated wastewater is discharged to the receiver
· idle – period during which excess sludge is removed
· standby – period during which the reactor waits for the next filling (optional)
Despite the seemingly complex process and construction, thanks to the use of a Polish-made controller, mammoth pump, and all air-powered components, there are no mechanical elements inside the tank. This ensures failure-free operation, provided nothing except toilet paper is discharged into the system. Items that must not be disposed of include:
· wet wipes ( including baby wipes )
· cigarette butts
· sanitary pads, tampons, and diapers
· hair
· bandages and medical dressings
· tablets, pills, and other solid-form medicines
· paints, solvents, adhesives, varnishes
· pesticides, herbicides, and other biocidal agents
· oils and fats
· brine produced during water softener regeneration
Avoiding the introduction of the above-mentioned wastes into the outflow is a key condition for maintaining the bacteria in the septic/biological part of the treatment plant in good condition, which has a significant, measurable impact on the operation of the entire system.
Thanks to its design, the treatment plant is resistant to uneven wastewater inflow, overloads, temperature fluctuations, and temporary lack of wastewater inflow (e.g., during vacation). It is also minimally sensitive to power outages. In the event of power loss, the controller adjusts the treatment phases according to the amount of wastewater in the plant and activates the appropriate phase depending on the accumulated volume.
– Safe design – no moving parts, no electric pumps, monolithic polyethylene (PE) tank ensuring tightness of the system.
– CE marked – tested by a notified body for compliance with PN–EN 12566-3 +A1:2009, ensuring high treatment efficiency verified by tests.
– Low sensitivity to power outages – the controller adapts treatment phases to the amount of incoming wastewater and activates the correct phase depending on the accumulated volume.
– Automated treatment process – allows full control over the treatment cycle; the controller adjusts to variations in wastewater inflow.
– Standby mode – allows the treatment plant to maintain operation even without wastewater inflow for up to 2 weeks.
– Long service life and reliability – PE tanks are monolithic and additionally reinforced internally with a steel frame.
For safe operation, the following components should be installed: fuse box.
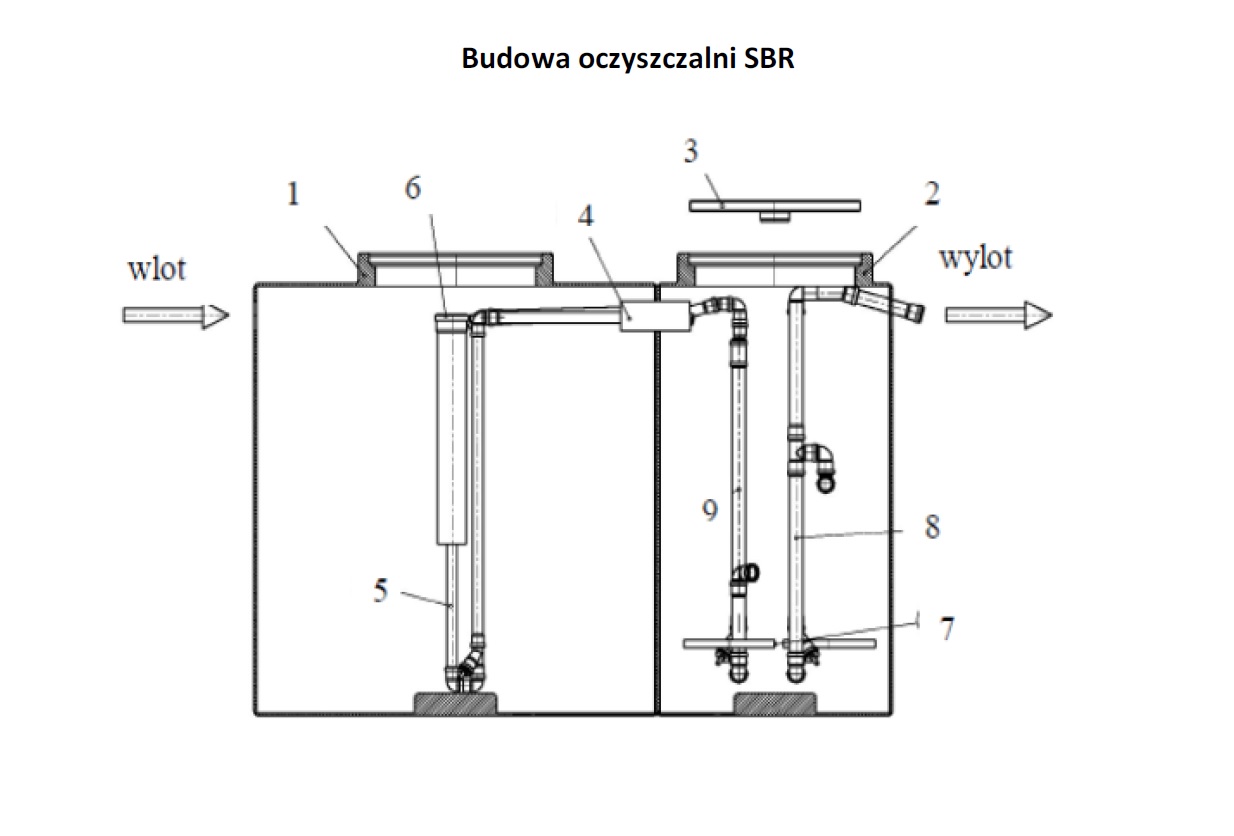
1. Primary settling tank / buffer tank
2. SBR reaction chamber
3. Manhole
4. Connection pipes DN 110
5. Compressed air lift
6. Sludge protection pipe
7. Active sludge aeration membranes
8. Compressed air lift
9. Compressed air lift
– SBR tank
– Riser with controller and lid
– Risers: DN 600 H-0.5 m – 2 pcs
– DN 600 lid, green color
– PVC pipe DN 110 grey, 1 m – 6 pcs
– Distribution manhole DN 400 H-0.7 m or DN 400 H-0.5 m or DN 400 H-1.1 m – 1 pc
– PVC elbow DN 110 87° grey – 5 pcs
– PVC drainage pipes DN 110 grey, 2 m – 18 pcs
– Aeration vent – 3 pcs
– Geotextile, width 0.5 m – 37 m
– PVC pipe DN 110 grey, 1 m – 3 pcs
– Distribution manhole DN 400 H-0.7 m – 1 pc
– PVC elbow DN 110 87° grey – 1 pc
– Tunnel infiltrators 150 L – 6 pcs
– PVC drainage pipes DN 110 grey, 2 m – 3 pcs
– Aeration vent – 1 pc
– Geotextile, width 2 m – 6 m
– PVC pipe DN 110 grey, 1 m – 3 pcs
– Distribution manhole DN 400 H-0.7 m – 1 pc
– PVC elbow DN 110 87° grey – 1 pc
– Tunnel infiltrators 300 L – 4 pcs
– Aeration vent – 1 pc
– Geotextile, width 2 m – 6 m
– Absorption well DN 600 H-1 m, perforated with side drainage holes
– DN 600 lid, green color
– Geotextile 2 m × 2 m
Installation nationwide by professional teams – arranged individually.
Have questions? Call us, and we will advise you on the optimal solution.
© Xymen 2023. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone
Projekt i realizacja: www.wertui.pl